Confocal microscopes have a very high spatial resolution among optical microscopes. In a modern process known as confocal laser scanning microscopy, they are widely used for cell imaging in the biomedical field and high-precision shape measurement in the semiconductor industry. The principle of confocal microscopy is based on a confocal optical system in which a point light source is projected onto a sample, while a pinhole and detector are placed at the image position of the sample.
The invention of the confocal microscope (1957, M. Minsky) actually came before the invention of the laser (1960). Initially, a lamp light source was used, however, lasers are now used in most cases because they are extremely bright, have high flux utilisation, and can provide monochromatic light of the wavelengths required for fluorescence observation, which is important in biomedical applications.
The history of the development of fluorescent reagents for fluorescence observation is strongly linked to the history of available light sources such as mercury lamps and gas lasers. For example, the use of fluorescent reagents with excitation wavelengths of 365 nm (i-line of mercury lamp) and 488 nm (argon ion laser) is a remnant of this history. Examples of excitation wavelengths used in biomedical confocal microscopy include 405, 488, 514, 561, 594, 640, and 647 nm, many of which use semiconductor lasers.
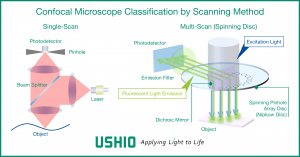
Types of confocal microscopes by scanning method
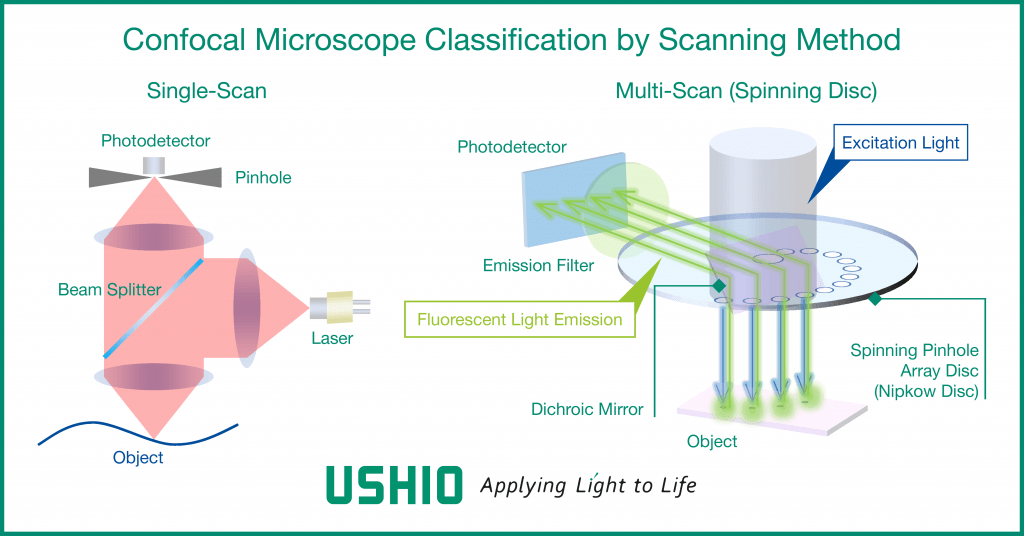
Since the confocal optical system is designed to detect only one spatial point, the detection position on the sample needs to be scanned to form an image. The scanning is achieved through a combination of moving the sample stage and beam scanning by using optics, such as a Galvano mirror. For single-scan type confocal microscopes with only one detection point, a transverse single-mode laser is used for reasons of light transmission and utilisation efficiency.
The spinning disc type confocal microscope enables scanning of a large number of detection points on a sample by means of a rotating disc with a large number (thousands to tens of thousands) of pinholes precisely arranged in a spiral manner. Since the spinning disc type scans by dividing the laser beam into multiple points, it is possible to suppress the deterioration of the cells to be observed (photo-toxicity) and the fading of fluorescent reagents due to light irradiation. Spinning-disc confocal microscopes can use multi-mode lasers in addition to transverse single-mode lasers.
Examples of laser products suitable for confocal microscopy
From Ushio’s wide range of laser diodes, here are a few examples of products suitable for confocal microscopy.
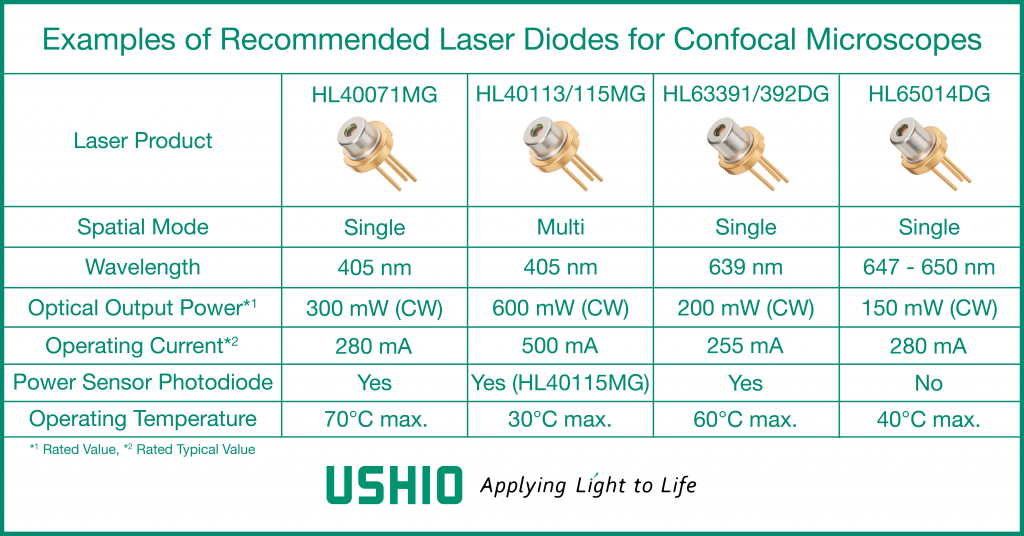
With a wavelength of 405 nm and an optical output power of 300 mW (CW), the HL40071MG is a violet laser diode that achieves the highest level of optical output power for a single-mode laser diode of this wavelength. It is suitable for fluorescence excitation in a wide range of biomedical fields including confocal microscopy.
HL40113MG/115MG, also at 405 nm, are multi-mode products with 600 mW output power and are suitable for use in spinning disc confocal microscopes as well as for situations where high power is required for fluorescence excitation. HL63391DG/392DG and HL65014DG are single-mode red laser diodes in the 640 nm and 647 nm bands, respectively, and can be applied to all types of confocal microscopes.
All of the products introduced here are available in a small TO-CAN package with a diameter of 5.6 mm. In addition, a photodiode is built into the CAN package to monitor the laser power, making it easy to control the optical output.
Contact Ushio for all confocal laser scanning microscopy needs
In addition to the products introduced here, Ushio offers a wide range of laser diodes to meet your needs. For more information, please visit the Ushio Laser Diode web page.
If you are interested in receiving more information about laser diodes for confocal laser scanning microscopy, please contact us through the following links:
Europe – Contact Form
United States – Contact Form
Asia – Contact Form